Asparaginase:
A sign of quality for yeast
Acrylamide fortification in foods which have been heated above 120°C is a problem often discussed in groceries' production.
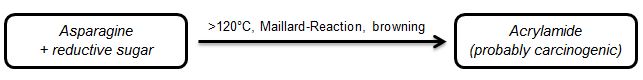
The EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) issued an updated risk assessment for acrylamide in food.
The german Bundesamt for Risk Assessment set a signal value of 1mg/kg.
Acrylamide fortification during baking processes can be reduced (up to 90%) by decomposition of asparagine in dough. Yeasts can act as natural sources for the asparagine dismantling enzyme asparaginase. Synthesis of asparaginase however depends on the yeast's strain and cultivation. Also yeast formulation (fresh or dry yeast) plays a certain role in sustaining the enzyme's activity.
We offer testing yeasts for asparaginase activity. Let the yeast you use be tested for asparaginase activity. The results will show if the yeast is capable of decomposing asparagine.
Send us an e-mail (info@amplab.de) to request a free quotation.



